Composers
Charles-François Gounod was a famous French composer and had a strong influence on the French composers of late 19th century. He was best known for his Ave Maria, Faust (an opera) and Roméo et Juliette (an opera). Roméo et Juliette Gounod’s very romantic and highly melodious work that was premiered in 1867.
Charles François Gounod was born in Paris in 1818. His mother, who was his first piano teacher; was a pianist and his father was a draftsman. Gounod was naturally gifted child and showed his first musical talent under the tutelage of his mother. After that Gounod entered the Paris Conservatoire and studied under Fromental Halévy.
Gounod wrote his first opera, “Sapho” that was based on the play by Goethe, in 1851. Although it was not very successful but it still considered as Gounod’s best-known work. Gounod’s earlier work included an improvisation of a melody over the C major Prelude (BWV 846) from The Well-Tempered Clavier, to which Gounod set the words of Ave Maria. Gounod also wrote Inno e Marcia Pontificale in 1859, that is now became the official national anthem of the Vatican City.
Gounod won the Prix de Rome for his cantata Fernand in 1837 and returned to Paris in 1843, after getting wide knowledge of earlier and contemporary music and stared working here, as an organist. In Paris, Gounod achieved considerable success in the theatre due to his most successful opera namely; Faust in 1859.
Gounod’s opera ‘Faust’ got the widest influence over many artists due to its heroic characterization and urging freedom from conventional restraints. Gounod's this opera was mainly concerned with Faust's seduction of Marguerite, who was the prey of the devil Mephistopheles. In the beginning, Faust faced controversy but it was minor. Many critics considered Faust as a great advancement over Gounod's previous works.
Similarly, Gounod's Roméo et Juliette got a great fame among François’s composition. Gounod’s Roméo et Juliette was composed on an operatic version of Shakespeare's play, staged in Paris in 1867.
Later on, he went to Italy for studying Palestrina music. Here he generated religious music of the sixteenth century. Most of his French songs were tined with the characteristics of Victorian era and present the setting of Victorian drawing- room.
In 1870, Gounod faced unprofitable interruption due to Franco- Prussian War and he went to England due to uncomfortable political situations and spent a period over there. In England Although Gounod’s talent putted influence over English vocal music and composed music to suit English sentimental taste but his work was not too best. Much of Gounod's music that was composed in England was vocal or choral in nature.
Gounod's also composed church music which were excessively sweet. Most of Gounod’s church music purely religious music, but not intended to compose for church use. This was composed for Ave Maria and was derived from the first Prelude of Bach's 48 Preludes and Fugues.
Gounod also wrote two symphonies which was his Petite symphony of 1885. Later on, he wrote Saltarello (an Italian dance akin to the Tarantella) in the same year. The recordings of Gounod’s best symphonies includes; the Orchestre national du Capitole de Toulouse and Sir Neville Marriner.
In the beginning of 1848, Gounod thought to return in his civil life with his early religious impulses, and wrote much on religious music. He began the compose "Messe Solennelle", which is also best known as the "Saint Cecilia Mass". Later on, Gounod’s "Messe Solennelle" which first performed in London in 1851; became very popular and raised Gounod’s reputation as a noteworthy composer throughout the world. This great French composer died on 18 October, 1893 at Saint-Cloud in France.
Recently Added
Refine by search
view allBiography
Charles-François Gounod was a famous French composer and had a strong influence on the French composers of late 19th century. He was best known for his Ave Maria, Faust (an opera) and Roméo et Juliette (an opera). Roméo et Juliette Gounod’s very romantic and highly melodious work that was premiered in 1867.
Charles François Gounod was born in Paris in 1818. His mother, who was his first piano teacher; was a pianist and his father was a draftsman. Gounod was naturally gifted child and showed his first musical talent under the tutelage of his mother. After that Gounod entered the Paris Conservatoire and studied under Fromental Halévy.
Gounod wrote his first opera, “Sapho” that was based on the play by Goethe, in 1851. Although it was not very successful but it still considered as Gounod’s best-known work. Gounod’s earlier work included an improvisation of a melody over the C major Prelude (BWV 846) from The Well-Tempered Clavier, to which Gounod set the words of Ave Maria. Gounod also wrote Inno e Marcia Pontificale in 1859, that is now became the official national anthem of the Vatican City.
Gounod won the Prix de Rome for his cantata Fernand in 1837 and returned to Paris in 1843, after getting wide knowledge of earlier and contemporary music and stared working here, as an organist. In Paris, Gounod achieved considerable success in the theatre due to his most successful opera namely; Faust in 1859.
Gounod’s opera ‘Faust’ got the widest influence over many artists due to its heroic characterization and urging freedom from conventional restraints. Gounod's this opera was mainly concerned with Faust's seduction of Marguerite, who was the prey of the devil Mephistopheles. In the beginning, Faust faced controversy but it was minor. Many critics considered Faust as a great advancement over Gounod's previous works.
Similarly, Gounod's Roméo et Juliette got a great fame among François’s composition. Gounod’s Roméo et Juliette was composed on an operatic version of Shakespeare's play, staged in Paris in 1867.
Later on, he went to Italy for studying Palestrina music. Here he generated religious music of the sixteenth century. Most of his French songs were tined with the characteristics of Victorian era and present the setting of Victorian drawing- room.
In 1870, Gounod faced unprofitable interruption due to Franco- Prussian War and he went to England due to uncomfortable political situations and spent a period over there. In England Although Gounod’s talent putted influence over English vocal music and composed music to suit English sentimental taste but his work was not too best. Much of Gounod's music that was composed in England was vocal or choral in nature.
Gounod's also composed church music which were excessively sweet. Most of Gounod’s church music purely religious music, but not intended to compose for church use. This was composed for Ave Maria and was derived from the first Prelude of Bach's 48 Preludes and Fugues.
Gounod also wrote two symphonies which was his Petite symphony of 1885. Later on, he wrote Saltarello (an Italian dance akin to the Tarantella) in the same year. The recordings of Gounod’s best symphonies includes; the Orchestre national du Capitole de Toulouse and Sir Neville Marriner.
In the beginning of 1848, Gounod thought to return in his civil life with his early religious impulses, and wrote much on religious music. He began the compose "Messe Solennelle", which is also best known as the "Saint Cecilia Mass". Later on, Gounod’s "Messe Solennelle" which first performed in London in 1851; became very popular and raised Gounod’s reputation as a noteworthy composer throughout the world. This great French composer died on 18 October, 1893 at Saint-Cloud in France.
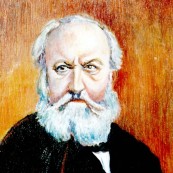














![The Opera Album 2011. [CD 2 of 2]](http://static.classicalm.com/repository/collection-cover/small/1345-img1369921777459572.jpg)

![Great Voices Of The Century - Sopranos, The Greatest Arias [CD1 of 4]](http://static.classicalm.com/repository/collection-cover/small/1401-img1403276640837603.jpg)
![Great Voices Of The Century - Sopranos, The Greatest Arias [CD2 of 4]](http://static.classicalm.com/repository/collection-cover/small/1402-img1403277217686408.jpg)
![Top 100 der Klassik [CD 2 of 5]](http://static.classicalm.com/repository/collection-cover/small/1365-img1372592354874210.jpg)
![Top 100 der Klassik [CD 4 of 5]](http://static.classicalm.com/repository/collection-cover/small/1367-img1372594763111487.jpg)












![Roberto Alagna. Mes Plus Grands Roles A L'Opera [CD1 of 3]](http://static.classicalm.com/repository/disk-cover/small/3160-img1383836322257038.jpg)


![Cecilia Bartoli – Sospiri [CD 2 of 2]](http://static.classicalm.com/repository/disk-cover/small/3054-img1375438347839669.jpg)